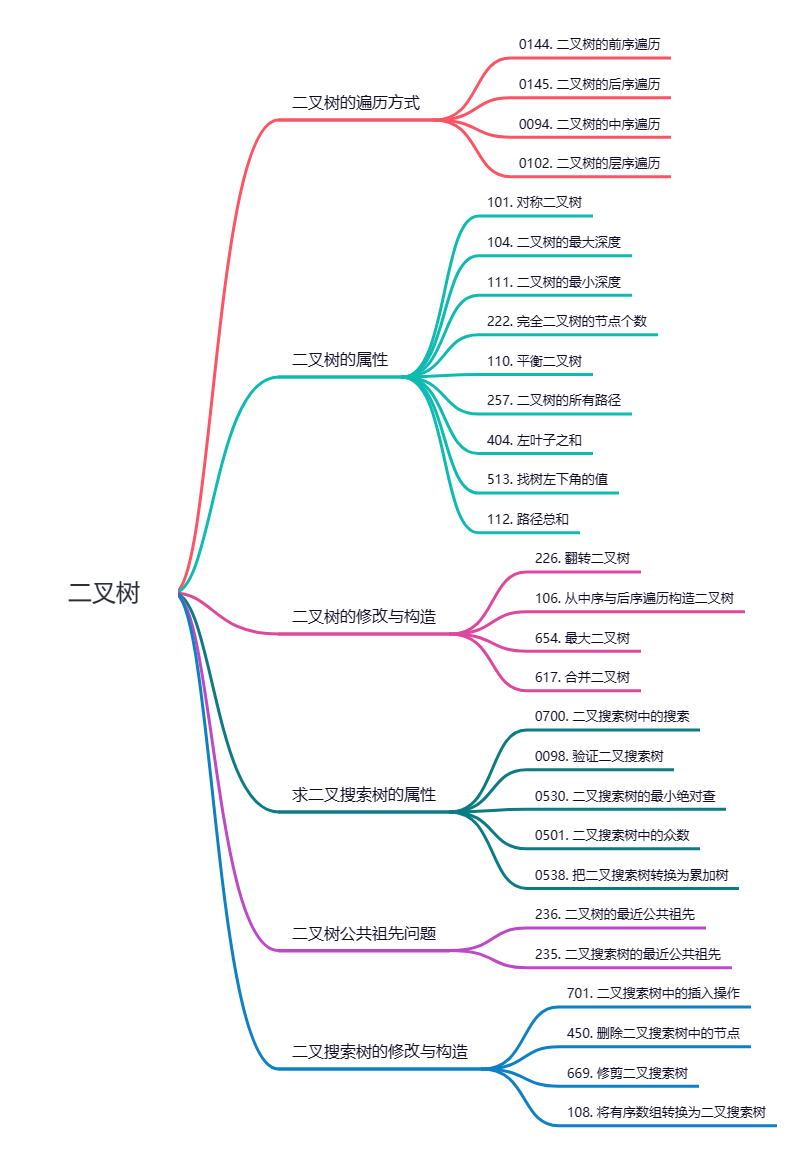
理论基础
二叉树的种类
满二叉树:只有度为0和度为2的结点,并且度为0的结点在同一层上。深度为k,有2k-1个节点
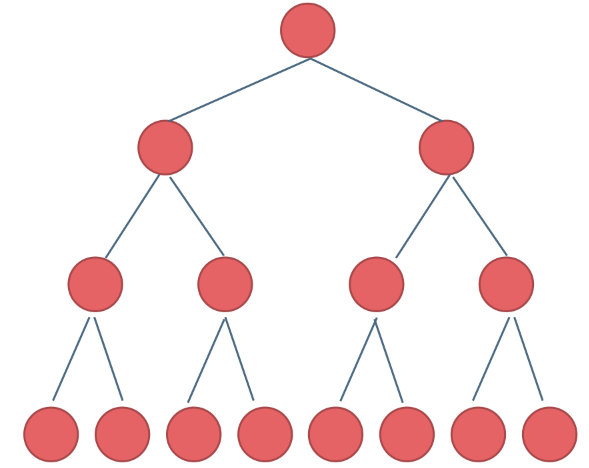
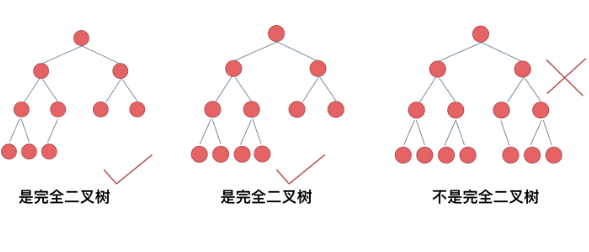
完全二叉树:除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层(h从1开始),则该层包含 1~ 2h-1 个节点
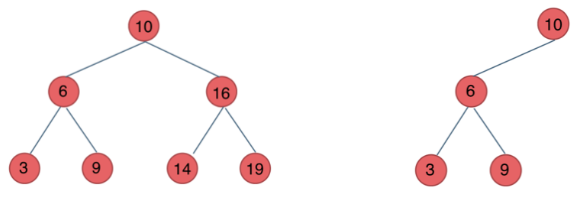
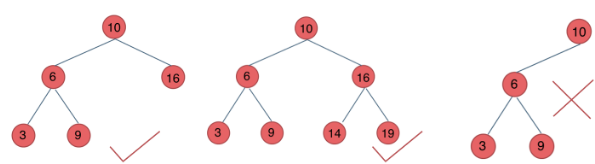
二叉搜索树:二叉搜索树有数值,是一个有序树,左<父<右
- 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
- 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
- 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树
平衡二叉搜索树:又被称为AVL(Adelson-Velsky and Landis)树,具有以下性质:是一棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树
二叉树的存储方式
二叉树可以链式存储,也可以顺序存储。链式存储用指针, 顺序存储用数组
用数组顺序存储的树中若父节点的下标是i,则左孩子是i * 2 + 1,右孩子是i * 2 + 2,节点i的父节点为(i - 1) / 2
二叉树的遍历方式
- 深度优先遍历:前中后序指的就是中间节点的位置
- 前序遍历(递归法,迭代法):中左右
- 中序遍历(递归法,迭代法):左中右
- 后序遍历(递归法,迭代法):左右中
- 广度优先遍历
二叉树节点的定义
1
2
3
4
5
|
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
|
二叉树的前序遍历
144. 二叉树的前序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它节点值的前序遍历
- 递归参数和返回值:传入当前遍历节点,不需要有返回值
- 终止条件:当前遍历的这个节点为空
- 单层递归逻辑:中左右,先取中点值,再递归
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
var res []int
func preorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) []int {
res = make([]int, 0)
dfs(root)
return res
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode) {
if cur == nil { // 节点为空
return
}
res = append(res, cur.Val) // 取值
dfs(cur.Left) // 左
dfs(cur.Right) // 右
}
|
二叉树的后序遍历
145. 二叉树的后序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
JZ33 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列_牛客题霸_牛客网
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
var res []int
func postorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) []int {
res = make([]int, 0)
dfs(root)
return res
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
dfs(cur.Left) // 左
dfs(cur.Right) // 右
res = append(res, cur.Val) // 中
}
|
二叉树的中序遍历
94. 二叉树的中序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
var res []int
func inorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) []int {
res = make([]int, 0)
dfs(root)
return res
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
dfs(cur.Left) // 左
res = append(res, cur.Val) // 中
dfs(cur.Right) // 右
}
|
二叉树的层序遍历
102. 二叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
JZ32 从上往下打印二叉树_牛客题霸_牛客网
JZ78 把二叉树打印成多行_牛客题霸_牛客网
用队列来实现一层一层遍历,初始时加入根节点,每次从队首取一个节点,遍历完本层所有节点,遇到节点有左右孩子就从队尾入队,直到队列为空
注意:若根为空,直接返回空
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
if root == nil {
return [][]int{}
}
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
res := make([][]int, 0)
queue = append(queue, root) // 根节点入队
for len(queue) > 0 { // 队列不为空
l := len(queue) // 本层节点数
temp := make([]int, 0) // 记录本层的节点值
for j := 0; j < l; j++ { // 遍历本层的所有节点
temp = append(temp, queue[0].Val) // 记录当前节点值
if queue[0].Left != nil { // 当前节点有左孩子
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Left) // 队尾入队
}
if queue[0].Right != nil { // 当前节点有右孩子
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Right) // 队尾入队
}
queue = queue[1:] // 当前节点队首出队
}
res = append(res, temp) // 将记录的本层节点值存入结果集
}
return res
}
|
二叉树的层序遍历 II
107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值自底向上的层序遍历(从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
用队列正常遍历树,每层结果存入结果集,最后反转结果集
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
func levelOrderBottom(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
if root == nil {
return [][]int{}
}
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
res := make([][]int, 0)
queue = append(queue, root) // 根节点入队
for len(queue) > 0 {
l := len(queue) // 记录该层节点数
temp := make([]int, 0) // 记录该层节点值
for j := 0; j < l; j++ {
temp = append(temp, queue[0].Val) // 记录节点值
if queue[0].Left != nil { // 有左孩子
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Left) // 左孩子入队
}
if queue[0].Right != nil { // 有右孩子
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Right) // 右孩子入队
}
queue = queue[1:] // 队首出队
}
res = append(res, temp) // 记录本层节点
}
for i, j := 0, len(res)-1; i < j; i, j = i+1, j-1 { // 反转结果集
res[i], res[j] = res[j], res[i]
}
return res
}
|
二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 锯齿形层序遍历 。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
func zigzagLevelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
res := make([][]int, 0)
if root == nil {
return res
}
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
queue = append(queue, root)
i := 1
for len(queue) != 0 {
l := len(queue)
temp := make([]int, 0)
for range l {
temp = append(temp, queue[0].Val)
if queue[0].Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Left)
}
if queue[0].Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Right)
}
queue = queue[1:len(queue)]
}
if i%2 == 0 {
for i, j := 0, len(temp)-1; i < j; i, j = i+1, j-1 {
temp[i], temp[j] = temp[j], temp[i]
}
}
i++
res = append(res, temp)
}
return res
}
|
二叉树的右视图
199. 二叉树的右视图 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值
BFS
用队列正常遍历树,遍历到每层最后的元素就存入结果集
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
func rightSideView(root *TreeNode) []int {
if root == nil {
return []int{}
}
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
res := make([]int, 0)
queue = append(queue, root) // 根节点入队
for len(queue) > 0 {
l := len(queue) // 记录本层节点数
for j := 0; j < l; j++ { // 遍历该层节点
if j == l-1 { // 本层最后一个节点
res = append(res, queue[0].Val) // 记录节点值
}
if queue[0].Left != nil { // 有左孩子
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Left) // 入队
}
if queue[0].Right != nil { // 有右孩子
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Right) // 入队
}
queue = queue[1:] // 出队
}
}
return res
}
|
DFS
前序遍历:中右左,递归参数带上目前深度,当目前深度等于结果集长度时,说明是第一次遇到这个深度的节点,由于先递归的右子树,所以该节点一定在右视图中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
func rightSideView(root *TreeNode) []int {
res := make([]int, 0)
var dfs func(cur *TreeNode, depth int)
dfs = func(cur *TreeNode, depth int) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
if depth == len(res) {
res = append(res, cur.Val)
}
dfs(cur.Right, depth+1)
dfs(cur.Left, depth+1)
}
dfs(root, 0)
return res
}
|
二叉树的层平均值
637. 二叉树的层平均值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个非空二叉树的根节点 root , 以数组的形式返回每一层节点的平均值。与实际答案相差 10-5 以内的答案可以被接受
用队列正常遍历,每遍历完一层就求平均值存入结果集,除数类型转换为float64
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
func averageOfLevels(root *TreeNode) []float64 {
if root == nil {
return []float64{}
}
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
res := make([]float64, 0)
queue = append(queue, root) // 根节点入队
for len(queue) > 0 {
l := len(queue) // 记录本层节点数
sum := 0 // 记录本层节点值总和
for j := 0; j < l; j++ {
sum += queue[0].Val // 记录节点值
if queue[0].Left != nil { // 有左孩子
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Left) // 入队
}
if queue[0].Right != nil { // 有右孩子
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Right) // 入队
}
queue = queue[1:] // 出队
}
res = append(res, float64(sum)/float64(l)) // 保存每层平均值
}
return res
}
|
N 叉树的层序遍历
429. N 叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历。(即从左到右,逐层遍历)
给定节点有两个属性,一个是节点值,另一个是该节点的孩子节点数组
用队列遍历,记录节点值后将该节点所有孩子节点入队
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
func levelOrder(root *Node) [][]int {
if root == nil {
return [][]int{}
}
queue := make([]*Node, 0)
res := make([][]int, 0)
queue = append(queue, root) // 根节点入队
for len(queue) > 0 {
l := len(queue)
temp := make([]int, 0) // 统计该层节点值
for i := 0; i < l; i++ { // 遍历该层节点
temp = append(temp, queue[0].Val) // 统计节点值
for j := 0; j < len(queue[0].Children); j++ { // 遍历孩子节点
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Children[j]) // 子节点入队
}
queue = queue[1:] // 队首出队
}
res = append(res, temp) // 记录该层节点值
}
return res
}
|
在每个树行中找最大值
515. 在每个树行中找最大值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,请找出该二叉树中每一层的最大值
用队列遍历,记录当前层最大值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
func largestValues(root *TreeNode) []int {
if root == nil {
return []int{}
}
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
res := make([]int, 0)
queue = append(queue, root) // 根节点入队
for len(queue) > 0 {
l := len(queue) // 记录本层节点
max := queue[0].Val // 记录本层最大值 默认为第一个节点值
for j := 0; j < l; j++ { // 遍历本层节点
if queue[0].Val > max {
max = queue[0].Val // 更新最大值
}
if queue[0].Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Left) // 左孩子入队
}
if queue[0].Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Right) // 右孩子入队
}
queue = queue[1:] // 队首出队
}
res = append(res, max) // 统计每层最大值
}
return res
}
|
填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树的根节点 ,每个节点有四个属性:节点值、左右孩子指针、右侧节点指针,要求填充每个节点的右侧节点指针,若没有右侧节点,则置空,初始状态下所有右侧指针都被置为空,最后返回根节点
思路一:BFS使用队列
用队列遍历,若非本层最后一个节点且队列存在下一个节点,则填充当前节点的右侧节点指针
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
if root == nil {
return root
}
queue := make([]*Node, 0)
// 根节点入队
queue = append(queue, root)
// 队非空
for len(queue) != 0 {
// 记录本层节点数
count := len(queue)
// 遍历本层节点
for i := 0; i < count; i++ {
// 头节点出队
cur := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
// 判是否为本层最右节点
if i != count-1 {
// 填充next
cur.Next = queue[0]
}
// 孩子入队
if cur.Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, cur.Left)
}
if cur.Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, cur.Right)
}
}
}
return root
}
|
思路二:DFS
常量级额外空间,使用前序遍历,通过上一层递归搭出来的线,进行本次搭线
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
dfs(root)
return root
}
func dfs(cur *Node) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
// 判左孩子非空
if cur.Left != nil {
cur.Left.Next = cur.Right
}
// 判右孩子非空且当前节点非最右节点
if cur.Right != nil && cur.Next != nil {
cur.Right.Next = cur.Next.Left
}
dfs(cur.Left)
dfs(cur.Right)
}
|
思路三:DFS+BFS
常量级额外空间,DFS遍历每层的最左节点,到倒数第二层结束;由于是完美二叉树,所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点,所以BFS遍历每层,填充当前节点左右孩子的next域
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
if root == nil {
return root
}
// 遍历每层最左节点
for cur := root; cur.Left != nil; cur = cur.Left {
// 遍历当前层节点
for node := cur; node != nil; node = node.Next {
// 填充当前节点的左孩子
node.Left.Next = node.Right
// 判当前节点是否为最右节点
if node.Next != nil {
// 填充当前节点的右孩子
node.Right.Next = node.Next.Left
}
}
}
return root
}
|
填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
和上一题不同之处:非完美二叉树,所有叶子节点不一定都在同一层,并非每个父节点都有两个子节点
思路一:DFS
用数组pre[i]记录第i层当前节点的前一个节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
// pre[i]:第i层当前节点的前一个节点
pre := []*Node{}
var dfs func(*Node, int)
dfs = func(cur *Node, depth int) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
if len(pre) == depth {
// 当前节点为本层首个节点
pre = append(pre, cur)
} else {
// 设置当前节点的前一节点的Next域
pre[depth].Next = cur
// 更新pre
pre[depth] = cur
}
// 继续递归遍历左右子树
dfs(cur.Left, depth+1)
dfs(cur.Right, depth+1)
}
dfs(root, 0)
return root
}
|
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为二叉树的节点个数。
- 空间复杂度:O(h),其中 h 为二叉树的高度,最坏情况下是 n
思路二:BFS
把每一层的节点,从左到右依次用 next 指针连接起来。
注意特判 root 为空的情况
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
if root == nil {
return root
}
queue := []*Node{root}
for queue != nil {
// 保存当前层所有节点
temp := queue
// 清空队列
queue = nil
// 遍历本层所有节点
for i, node := range temp {
// 从本层第二个节点开始连接前一节点与当前节点
if i > 0 {
temp[i-1].Next = node
}
// 当前节点的左右孩子入队
if node.Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.Right)
}
}
}
return root
}
|
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为二叉树的节点个数。
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
思路三:DFS + BFS
DFS遍历每层的最左节点,BFS遍历每层,把下一层的节点连接起来
这样每一层都连接成一个链表了,知道链表头,就能访问这一层的所有节点,无需存储下一层的节点。
注意:代码实现时,可以用一个虚拟节点来表示每层「第一个节点之前的节点」,从而减少一些关于空节点的判断逻辑。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
// 作为每一层的最左节点的前一节点
dummyNode := new(Node)
// 遍历每一层的最左节点
for start := root; start != nil; start = dummyNode.Next {
// 重置dummyNode的Next域
dummyNode.Next = nil
// 记录当前节点下一层每个节点的前一节点
pre := dummyNode
// 遍历当前层的所有节点
for cur := start; cur != nil; cur = cur.Next {
// 判当前节点的左孩子是否非空
if cur.Left != nil {
// 置当前节点的左孩子的前一节点的next域
pre.Next = cur.Left
// 更新pre
pre = cur.Left
}
if cur.Right != nil {
pre.Next = cur.Right
pre = cur.Right
}
}
}
return root
}
|
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为二叉树的节点个数。
- 空间复杂度:O(1)。只用到若干额外变量
二叉树的最大深度
104. 二叉树的最大深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
JZ55 二叉树的深度_牛客题霸_牛客网
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度
BFS:用队列层序遍历,每遍历一层,深度加一
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
res := 0
queue = append(queue, root)
for len(queue) > 0 {
l := len(queue)
res++
for j := 0; j < l; j++ {
if queue[0].Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Left)
}
if queue[0].Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Right)
}
queue = queue[1:]
}
}
return res
}
|
DFS:后序、分治 求得根节点的高度
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
left := maxDepth(root.Left)
right := maxDepth(root.Right)
if left > right {
return left + 1
}
return right + 1
}
|
N 叉树的最大深度
559. N 叉树的最大深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个根节点,找出其最大深度,节点有两个属性,一个是节点值,另一个是子节点数组
用队列层序遍历,记录层数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
func maxDepth(root *Node) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
queue := make([]*Node, 0)
queue = append(queue, root) // 根节点入队
res := 0
for len(queue) > 0 {
l := len(queue)
res++ // 层数加一
for j := 0; j < l; j++ {
if len(queue[0].Children) > 0 {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Children...) // 子节点入队
}
queue = queue[1:] // 队首出队
}
}
return res
}
|
二叉树的最小深度
111. 二叉树的最小深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度,最小深度是指从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量
用队列遍历,若没有左右孩子,说明遇到叶子节点,直接返回层数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
func minDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
res := 0
queue = append(queue, root)
for len(queue) > 0 {
l := len(queue)
res++
for j := 0; j < l; j++ {
if queue[0].Left == nil && queue[0].Right == nil { // 遇到叶子节点
return res
}
if queue[0].Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Left)
}
if queue[0].Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Right)
}
queue = queue[1:]
}
}
return res
}
|
dfs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
func minDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
// 判当前节点是否无左孩子
if root.Left == nil {
// 直接返回右子树高度+1
return minDepth(root.Right) + 1
}
if root.Right == nil {
return minDepth(root.Left) + 1
}
// 左右孩子都有,返回俩孩子最小高度+1
return min(minDepth(root.Left), minDepth(root.Right))+1
}
|
翻转二叉树
226. 翻转二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
JZ27 二叉树的镜像_牛客题霸_牛客网
给定一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,左右翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点
只要将每个节点的左右孩子翻转,就可以达到整体翻转的效果
注意:若兄弟节点为空,也需要反转
dfs
到中时翻转左右孩子,前后序都可以,中序不行,中序会把某些节点的左右孩子翻转两次,因为中会把左右翻转,然后到右,右是之前的左,已经在中之前翻转过了,等于把原来的左翻转了两次
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
func invertTree(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
dfs(root)
return root
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
cur.Left, cur.Right = cur.Right, cur.Left // 中的左右孩子翻转
dfs(cur.Left) // 左
dfs(cur.Right) // 右
}
|
bfs
用队列遍历,入队前先交换左右孩子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
func invertTree(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return root
}
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
queue = append(queue, root) // 根节点入队
for len(queue) > 0 {
l := len(queue)
for j := 0; j < l; j++ { // 遍历本层节点
queue[0].Left, queue[0].Right = queue[0].Right, queue[0].Left // 交换孩子节点
if queue[0].Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Left) // 左孩子入队
}
if queue[0].Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Right) // 右孩子入队
}
queue = queue[1:] // 出队
}
}
return root
}
|
对称二叉树
101. 对称二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称
BFS
用队列层序遍历,遇到无孩子则自己填充一个特殊值节点加入队列,保存每层节点都是满的,不然有空位置没法比较,然后双指针指向首尾逐个判断该层节点是否对称,最后该层节点全部出队
注意:
- 填充节点要先判断该节点是否是特殊值节点,若是,则不再填充,否则会死循环
- 填充节点要注意先左后右的顺序,不能在最后再填充
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool {
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
queue = append(queue, root) // 根节点入队
for len(queue) > 0 {
l := len(queue) // 本层节点数
for j := 0; j < l; j++ { // 遍历本层节点
specNode := new(TreeNode)
specNode.Val = 101
if queue[j].Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[j].Left) // 左孩子入队
} else if queue[j].Left == nil && queue[j].Val != 101 {
queue = append(queue, specNode) // 特殊节点入队
}
if queue[j].Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[j].Right) // 右孩子入队
} else if queue[j].Right == nil && queue[j].Val != 101 {
queue = append(queue, specNode) // 特殊节点入队
}
}
for idx1, idx2 := 0, l-1; idx1 < idx2; idx1, idx2 = idx1+1, idx2-1 { // 逐个比较该层节点
if queue[idx1].Val != queue[idx2].Val {
return false // 有节点不对称
}
}
queue = queue[l:] // 本层节点出队
}
return true
}
|
DFS
二叉树是否对称要比较的是根节点的左右子树是不是相互翻转的;在递归遍历的过程中同时遍历两棵树;本题只能是后序遍历,一个树的遍历顺序是左右中,另一个树的遍历顺序是右左中
- 递归参数和返回值:两个递归参数,一个是左子树节点,另一个是右子树节点,返回值是布尔值
- 终止条件:若左右节点不全为空或值不相等,则返回
false,若左右节点全为空,则返回true
- 单层递归:处理左右节点都不为空,且数值相同的情况比较左子树的左节点与右子树的右节点(外侧)和左子树的右节点与右子树的左节点(内侧)
先外侧向深逐个比较,若遇到不相等的,则false会层层向上传递;若相等,则会继续向下比较,外侧比较完后比较内层
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool {
return dfs(root.Left, root.Right)
}
func dfs(left *TreeNode, right *TreeNode) bool {
if (left == nil && right != nil) || (left != nil && right == nil) {
return false // 左右节点不全为空
} else if left == nil && right == nil {
return true // 左右节点全为空
} else if left.Val != right.Val {
return false // 左右节点值不相等
}
return dfs(left.Left, right.Right) && dfs(left.Right, right.Left) // 继续比较
}
|
相同的树
100. 相同的树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定两棵二叉树的根节点 p 和 q ,如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的,检验这两棵树是否相同
与上题不同在于:上题是比较对称位置节点值是否相同,本题是比较相同位置节点值是否相等
思路:中序同时遍历俩树,若遇到俩节点都为空,则返回true,若遇到俩节点一个空另一个非空,说明不相同则返回false,若俩节点值不同,则返回false,最后向左向右递归,返回值用return和&&接住
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
func isSameTree(p *TreeNode, q *TreeNode) bool {
// 俩节点都为空
if p == nil && q == nil {
return true
}
// 俩节点一个空另一个非空
if p == nil || q == nil {
return false
}
// 俩节点值不同
if p.Val != q.Val {
return false
}
// 向左向右递归
return isSameTree(p.Left, q.Left) && isSameTree(p.Right, q.Right)
}
|
另一棵树的子树
572. 另一棵树的子树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定两棵二叉树 root 和 subRoot ,检验 root 中是否包含和 subRoot 具有相同结构和节点值的子树。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false
本题还是比较树是否相等,遍历root,将每个节点作为根,与subRoot比较
注意:力扣中全局变量要重新初始化,因为和上一用例是同一命名空间
DFS+DFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
func isSubtree(A *TreeNode, B *TreeNode) bool {
if A == nil {
return false
}
return check(A, B) || isSubtree(A.Left, B) || isSubtree(A.Right, B)
}
func check(cur1, cur2 *TreeNode) bool {
if cur1 == nil && cur2 == nil {
return true
}
if cur1 == nil || cur2 == nil {
return false
}
if cur1.Val == cur2.Val {
return check(cur1.Left, cur2.Left) && check(cur1.Right, cur2.Right)
}
return false
}
|
进阶:树哈希(字节劝退题)
把每个子树都映射成一个唯一的数,如果 t 对应的数字和 s 中任意一个子树映射的数字相等,则 t 是 s 的某一棵子树。
子结构判断
LCR 143. 子结构判断 - 力扣(LeetCode)
JZ26 树的子结构_牛客题霸_牛客网
与上一题区别是,本题是子结构,不是子树,要求更低
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
func isSubStructure(A *TreeNode, B *TreeNode) bool {
if A == nil || B == nil {
return false
}
return check(A, B) || isSubStructure(A.Left, B) || isSubStructure(A.Right, B)
}
func check(cur1, cur2 *TreeNode) bool {
if cur2 == nil {
return true
}
if cur1 == nil || cur1.Val != cur2.Val {
return false
}
return check(cur1.Left, cur2.Left) && check(cur1.Right, cur2.Right)
}
|
完全二叉树的节点个数
222. 完全二叉树的节点个数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一棵完全二叉树的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数
DFS 后序 分治 完全二叉树、满二叉树性质(推荐)
- 满二叉树性质:总节点数为 2h-1
- 完全二叉树性质:除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置
思路:统计 root 节点左右子树的高度,分别记为 leftHeight 和 rightHeight,有两种情况:
leftHeight == rightHeight:说明左子树必定已经填满了,是一棵满二叉树。所以左子树的节点总数可以直接得到,是 2left - 1,加上当前 root 节点,则正好是 2left。再对右子树进行递归统计。leftHeight != rightHeight:说明此时最后一层不满,但倒数第二层已经满了,可以直接得到右子树的节点个数。同理,右子树节点 + root 节点,总数为 2right。再对左子树进行递归查找。
注意:计算 2h,最快的方法是移位计算,因为运算符的优先级问题,记得加括号
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
func countNodes(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
leftH, rightH := 1, 1
leftNode := root.Left
rightNode := root.Right
// 向左找最大深度
for leftNode != nil {
leftNode = leftNode.Left
leftH++
}
// 向右找最大深度
for rightNode != nil {
rightNode = rightNode.Right
rightH++
}
// 判断当前节点的作为根节点的树是否为满二叉树
if leftH == rightH {
// 返回当前树的总结点数
return (1 << leftH) - 1
}
// 继续递归找满二叉树 +1是当前节点
return countNodes(root.Left) + countNodes(root.Right) + 1
}
|
- 时间复杂度:O(log n × log n)
- 空间复杂度:O(log n)
DFS遍历(不推荐)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
func countNodes(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
l := countNodes(root.Left)
r := countNodes(root.Right)
return l + r + 1
}
|
BFS遍历(不推荐)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
func countNodes(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
queue = append(queue, root) // 根节点入队
res := 0
for len(queue) > 0 {
l := len(queue)
res += l // 逐层累加节点数
for j := 0; j < l; j++ {
if queue[0].Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Left) // 左孩子入队
}
if queue[0].Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Right) // 右孩子入队
}
queue = queue[1:] // 队首出队
}
}
return res
}
|
平衡二叉树
110. 平衡二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
JZ79 判断是不是平衡二叉树_牛客题霸_牛客网
给定一个二叉树的根节点,判断它是否是平衡二叉树(该树所有节点的左右子树的高度相差不超过 1)
- 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数。
- 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数。
根节点深度是1,叶子节点高度是1
求深度可以从上到下去查,可以前序遍历(中左右);高度只能从下到上去查,只能后序遍历(左右中)
- 递归函数的参数和返回值:参数是当前传入节点;返回值是以当前传入节点为根节点的树的高度;若以当前传入节点为根节点的二叉树已经不是二叉平衡树了,返回-1来标记不符合平衡树规则
- 终止条件:遇到空节点
- 单层递归:分别求出其左右子树的高度,然后如果差值小于等于1,则返回当前二叉树的高度,否则返回-1,表示已经不是二叉平衡树了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
// 写法一
func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
height := getHeight(root)
if height == -1 {
return false // 不是平衡二叉树
}
return true
}
func getHeight(cur *TreeNode) int {
if cur == nil {
return 0
}
leftHeight := getHeight(cur.Left) // 左
if leftHeight == -1 {
return -1 // 左子树已经不是平衡二叉树
}
rightHeight := getHeight(cur.Right) // 右
if rightHeight == -1 {
return -1 // 右子树已经不是平衡二叉树
}
if leftHeight-rightHeight > 1 || rightHeight-leftHeight > 1 {
return -1 // 当前节点左右子树高度差大于1
}
return max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1 // 返回当前节点高度(叶子节点初始为1)
}
// 写法二
func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
return dfs(root) != -1
}
// 返回当前节点为根节点的树高度
func dfs(cur *TreeNode) int {
// 遇到空高度为0
if cur == nil {
return 0
}
// 向左右递归
leftHeight := dfs(cur.Left)
rightHeight := dfs(cur.Right)
// 判断是否平衡
if leftHeight == -1 || rightHeight == -1 || leftHeight-rightHeight > 1 || rightHeight-leftHeight > 1 {
return -1
}
// 返回当前节点为根的树高度
return max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1
}
|
二叉树的所有路径
257. 二叉树的所有路径 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径
题目要求从根节点到叶子的路径,所以需要前序遍历;需要回溯来回退一个路径再进入另一个路径
DFS思路一
- 递归函数参数以及返回值:参数只需要当前节点,路径和结果用全局变量,不需要返回值
- 终止条件:遇到空节点或找到叶子节点(即当前节点的左右孩子都为空)
- 单层递归:若不是空节点,则将当前节点放进path中;然后是判断是否为叶子节点,若为叶子节点,则收集路径,不再往下递归,直接回溯,若不是叶子节点则继续向下递归;最后递归结束后要做一次回溯,表示当前节点的左右节点已经递归遍历结束,需要从路径中删除当前节点,回到当前节点的父节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
var path []int
var intRes [][]int
func binaryTreePaths(root *TreeNode) []string {
path = make([]int, 0)
intRes = make([][]int, 0)
dfs(root)
res := make([]string, 0)
for _, nums := range intRes { // 遍历各条路径
temp := "" // 存放一条路径
for _, num := range nums { // 遍历路径中各点值
if temp == "" {
temp += strconv.Itoa(num) // 是第一个节点
} else {
temp += "->" + strconv.Itoa(num)
}
}
res = append(res, temp) // 记录该条路径
}
return res
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
path = append(path, cur.Val) // 该节点值计入路径
if cur.Left == nil && cur.Right == nil { // 遇到叶子节点
temp := make([]int, len(path))
copy(temp, path)
intRes = append(intRes, temp) // 当前路径加入结果集
path = path[:len(path)-1] // 回溯
return
}
dfs(cur.Left) // 左
dfs(cur.Right) // 右
path = path[:len(path)-1] // 回溯
}
|
DFS思路二
- 递归函数参数以及返回值:参数需要当前节点、路径,结果集为全局变量,不需要返回值
- 终止条件:找到叶子节点,即当前节点的左右孩子都为空
- 单层递归:若找到叶子节点,则将当前路径及当前叶子节点加入结果集,若不是叶子节点,则计入路径;然后判断如果当前节点是否存在左右孩子,若有则向其递归
注意:
- 由于终止条件只判断了是否为叶子节点,所以在单层递归中需要先判断是否存在孩子再递归,避免遇到空节点被当作叶子节点
- 由于使用路径作为传入参数,所以递归中隐含有路径回溯
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
var res []string
func binaryTreePaths(root *TreeNode) []string {
path := ""
res = make([]string, 0)
dfs(root, path)
return res
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode, path string) {
if cur.Left == nil && cur.Right == nil { // 遇到叶子节点
temp := path + strconv.Itoa(cur.Val) // 将叶子节点加入路径
res = append(res, temp) // 该条路径加入结果集
return
}
path += strconv.Itoa(cur.Val) + "->" // 当前节点值计入路径(中)
if cur.Left != nil {
dfs(cur.Left, path) // 左
}
if cur.Right != nil {
dfs(cur.Right, path) // 右
}
}
|
左叶子之和
404. 左叶子之和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定二叉树的根节点 root ,返回所有左叶子之和
无法判断当前节点是不是左叶子,只能通过当前节点判断其左孩子是不是叶子节点,从而确定左叶子节点
DFS思路一:前序
- 递归参数和返回值:参数传入当前节点,不需要返回值,结果集作为全局变量
- 终止条件:当前节点的左孩子为叶子节点
- 单层递归:判断当前节点是否存在左孩子,若存在,则判断是否为叶子节点,若是则加入结果集,然后判断是否有右孩子,若有则继续向下递归,若没有右孩子则返回;若当前节点存在左孩子但不是叶子节点,则继续向下递归;若当前节点不存在左孩子,则判断是否右孩子,若存在则递归,不存在则返回
注意:终止返回隐含在if逻辑中,不用显式写出return
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
var res int
func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
res = 0
dfs(root)
return res
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode) {
if cur.Left != nil { // 当前节点左孩子不为空
if cur.Left.Left == nil && cur.Left.Right == nil { // 当前节点左孩子为叶子节点
res += cur.Left.Val // 记录和
if cur.Right != nil { // 当前节点有右孩子
dfs(cur.Right) // 右
}
} else { // 当前节点左孩子不是叶子节点
dfs(cur.Left) // 左
if cur.Right != nil {
dfs(cur.Right) // 右
}
}
} else { // 当前节点左孩子为空
if cur.Right != nil { // 当前节点右孩子不为空
dfs(cur.Right) // 右
}
}
}
// 写法二
func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
res := 0
var dfs func(*TreeNode)
dfs = func(cur *TreeNode) {
// 当前节点为空直接返回
if cur == nil {
return
}
// 当前节点的左子节点为叶子节点
if cur.Left != nil && cur.Left.Left == nil && cur.Left.Right == nil {
res += cur.Left.Val
// 只向当前节点的右子节点遍历
dfs(cur.Right)
} else {
// 正常遍历
dfs(cur.Left)
dfs(cur.Right)
}
}
dfs(root)
return res
}
|
DFS思路二:后序
- 递归参数和返回值:参数传入当前节点,返回值为左叶子之和
- 终止条件:当前节点为空节点,返回0;
- 单层递归:当遇到左叶子节点的时候,记录数值,然后通过递归求取左子树左叶子之和,和 右子树左叶子之和,相加便是整个树的左叶子之和
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
res := dfs(root)
return res
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode) int {
if cur == nil {
return 0
}
leftValue := dfs(cur.Left) // 当前节点的左子树中收集的左叶子和(左)
if cur.Left != nil && cur.Left.Left == nil && cur.Left.Right == nil { // 当前节点存在左节点且为叶子节点
leftValue = cur.Left.Val // 收集当前节点左叶子值
}
rightValue := dfs(cur.Right) // 当前节点的右子树中收集的左叶子和(右)
return leftValue + rightValue // 中
}
|
找树左下角的值
513. 找树左下角的值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的最底层最左边节点的值
用队列层序遍历,维护一个整型变量,仅保存当前遍历层的第一个节点值,当队列为空时,整型变量值就是最底层最左边的节点值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
func findBottomLeftValue(root *TreeNode) int {
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
queue = append(queue, root) // 根节点入队
res := 0
for len(queue) > 0 {
l := len(queue) // 当前层节点数
res = queue[0].Val // 记录本层首节点值
for j := 0; j < l; j++ {
if queue[0].Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Left) // 左孩子入队
}
if queue[0].Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Right) // 右孩子入队
}
queue = queue[1:] // 队首出队
}
}
return res
}
|
路径总和
112. 路径总和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个根节点 root 和整数 targetSum ;判断该树中根节点到叶子节点的路径中是否存在节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 的路径;如果存在返回 true ,否则返回 false
求根节点到叶子节点,用前序遍历
DFS思路一
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是当前节点、路径和、目标路径和,不需要返回值,用全局变量标记是否找到控制终止,回溯隐含在逻辑中
- 终止条件:遇到空节点或找到目标路径
- 单层递归:先判断是否遇到空节点或找到目标路径,若是直接返回,若不是则将当前节点值加入路径值总和,然后判断当前路径是否为根节点到叶子节点的路径且路径和等于目标和,若是直接返回,否则向下继续递归
注意:
- 必须是根节点到叶子节点的路径,不能是根节点到任意节点的一条路径
- 若终止条件没有判断是否是空节点,则在向下递归前需要先判断是否有该孩子;若仅判断为不是叶子节点就向下递归,会导致访问空指针的错误
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
var isOk bool
func hasPathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) bool {
sum := 0
isOk = false // 初始为未找到
dfs(root, sum, targetSum)
return isOk
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode, sum int, targetSum int) {
if cur == nil {
return // 到空节点都没找到
}
if isOk {
return // 找到目标路径和
}
sum += cur.Val // 记录路径和(中)
if cur.Left == nil && cur.Right == nil && sum == targetSum { // 当前节点是叶子节点且路径和等于目标和
isOk = true // 找到目标路径和
return
}
dfs(cur.Left, sum, targetSum) // 左
dfs(cur.Right, sum, targetSum) // 右
}
|
DFS思路二
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是当前节点、目标路径和,返回值为布尔值,标记是否找到目标路径
- 终止条件:遇到空节点或找到目标路径
- 单层递归:先判断是否遇到空节点或找到目标路径,若是直接返回,若不是则将目标和减去当前节点值,然后向下继续递归,只要左右子树中有一个找到就返回
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
func hasPathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) bool {
return dfs(root, targetSum)
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode, targetSum int) bool {
if cur == nil {
return false // 遇到空节点都没找到
}
if cur.Left == nil && cur.Right == nil && cur.Val == targetSum {
return true // 找到目标路径
}
return hasPathSum(cur.Left, targetSum-cur.Val) || hasPathSum(cur.Right, targetSum-cur.Val)
}
|
路径总和 II
113. 路径总和 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是当前节点、目标和、路径;不需要返回值;结果集是全局变量,回溯隐含在逻辑中
- 终止条件:遇到空节点
- 单层递归:累加当前路径和、更新路径、继续向下递归
注意:Go中slice、map、channel、function、pointer是引用传递,是浅拷贝,只把变量里面存的内存地址拷贝了,所指向的真实值并没拷贝
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
var res [][]int
func pathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) [][]int {
path := make([]int, 0)
res = make([][]int, 0)
dfs(root, path, targetSum)
return res
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode, path []int, targetSum int) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
path = append(path, cur.Val) // 更新路径(中)
if cur.Left == nil && cur.Right == nil && targetSum == cur.Val { // 是叶子节点且是目标路径
temp := make([]int, len(path))
copy(temp, path)
res = append(res, temp) // 记录一条目标路径
return
}
dfs(cur.Left, path, targetSum-cur.Val) // 左
dfs(cur.Right, path, targetSum-cur.Val) // 右
}
|
从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树的中序遍历和后序遍历序列,要求构造这颗二叉树并返回根节点
先将后序序列中最后一个为根节点明确;然后在中序序列中找到根节点的值,分割出其左边的所有节点作为左子树序列,右边的所有节点作为右子树序列;再回后序序列中删除最后一个节点然后按照中序中切割出的左子树序列长度来切割出后序序列中对应的左子树序列和右子树序列;最后递归处理根节点的左子树序列和右子树序列
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是中序序列和后序序列;返回值是根节点
- 终止条件:后序序列为空或后序序列中只有一个节点
- 单层递归:先判断后序是否为空,若为空说明构造完成直接返回,否则创建当前树的根节点并赋值;然后再判断后序序列是否只剩一个值,若是说明是叶子节点,直接返回该节点;若不是则在中序序列中找到根节点,分割出其左边的所有节点作为左子树序列,右边的所有节点作为右子树序列;再回后序序列中删除最后一个节点然后按照中序中切割出的左子树序列长度来切割出后序序列中对应的左子树序列和右子树序列;最后继续向下处理根节点的左子树序列和右子树序列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
func buildTree(inorder []int, postorder []int) *TreeNode {
if len(postorder) == 0 {
return nil // 构造完成
}
root := new(TreeNode) // 构造根节点
root.Val = postorder[len(postorder)-1] // 取后序最后一个作为根值
if len(postorder) == 1 {
return root // 返回该叶子节点
}
delimiterIndex := 0 // 标记中序的分割索引
for i, v := range inorder {
if v == root.Val {
delimiterIndex = i // 记录中序分割点
break
}
}
leftInorder := inorder[:delimiterIndex] // 中序的左子树序列
rightInorder := inorder[delimiterIndex+1:] // 中序的右子树序列
leftPostorder := postorder[:len(leftInorder)] // 后序的左子树序列
rightPostorder := postorder[len(leftInorder) : len(postorder)-1] // 后序的右子树序列
root.Left = buildTree(leftInorder, leftPostorder) // 构造根节点的左子树
root.Right = buildTree(rightInorder, rightPostorder) // 构造根节点的右子树
return root
}
|
从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
JZ7 重建二叉树_牛客题霸_牛客网
给定二叉树的前序和中序序列,构造该二叉树并返回根节点
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是前序序列和中序序列,返回值是根节点
- 终止条件:前序为空或前序长度为1
- 单层递归:判断前序是否为空,若是说明构造完成,直接返回空节点;构造一个节点,赋值为当前前序第一个值;判断前序长度是否为1,若是说明是叶子节点,直接返回该节点;从中序序列中找到该节点值,其左边所有值作为左子树中序序列,右边所有值作为右子树中序序列;删除前序序列中首值,按照左子树序列长度从前序序列中截取左子树前序序列,右边剩下的作为右子树前序序列;由四个序列分别递归构造当前节点的左子树和右子树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
func buildTree(preorder []int, inorder []int) *TreeNode {
if len(preorder) == 0 {
return nil // 构造完毕
}
root := new(TreeNode)
root.Val = preorder[0] // 前序首值作为根节点值
if len(preorder) == 1 {
return root // 叶子节点
}
delimitIndex := 0 // 记录中序分割点
for i, v := range inorder {
if v == preorder[0] {
delimitIndex = i // 标记中序分割点
break
}
}
leftInorder := inorder[:delimitIndex] // 左子树的中序序列
rightInorder := inorder[delimitIndex+1:] // 右子树的中序序列
leftPreOrder := preorder[1 : len(leftInorder)+1] // 左子树的前序序列
rightPreOrder := preorder[len(leftInorder)+1:] // 右子树的前序序列
root.Left = buildTree(leftPreOrder, leftInorder) // 构造根节点的左子树
root.Right = buildTree(rightPreOrder, rightInorder) // 构造根节点的右子树
return root
}
// 简化
func buildTree(preorder []int, inorder []int) *TreeNode {
if len(preorder) == 0 {
return nil
}
newNode := &TreeNode{Val: preorder[0]}
idx := 0
for i, v := range inorder {
if v == preorder[0] {
idx = i
}
}
newNode.Left = buildTree(preorder[1:idx+1], inorder[:idx])
newNode.Right = buildTree(preorder[idx+1:], inorder[idx+1:])
return newNode
}
|
最大二叉树
654. 最大二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个数组,将数组中的最大值作为根节点,最大值左边所有数作为左子树,右边所有数作为右子树,递归的构建二叉树,返回根节点
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是给定数组,返回值是构造出的节点
- 终止条件:给定数组为空或只剩一个节点
- 单层递归:判断给定数组是否为空,若是说明构造完成直接返回;初始化一个节点,赋值为给定数组的最大值;判断给定数组是否只剩一个节点,若是说明是叶子节点直接返回该叶子节点;截取给定数组最大值左边的所有数和右边的所有树,递归地构建当前节点的左右子树;最后返回当前节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
func constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums []int) *TreeNode {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return nil // 构造完成
}
maxIndex := 0
for i, v := range nums {
if v > nums[maxIndex] {
maxIndex = i // 获取数组中最大值下标
}
}
root := new(TreeNode)
root.Val = nums[maxIndex] // 根节点赋值
if len(nums) == 1 {
return root // 叶子节点
}
root.Left = constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums[:maxIndex]) // 构造根节点左子树
root.Right = constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums[maxIndex+1:]) // 构造根节点右子树
return root
}
|
合并二叉树
617. 合并二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定两个二叉树,对其进行合并,值之和作为合并后节点值,一方为空直接覆盖,返回合并后树的根节点
思路一:构造新节点
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是两个二叉树的当前节点,返回值是新的节点
- 终止条件:两个二叉树的当前节点都为空
- 单层递归:判断两个二叉树的当前节点是否都为空,若是则直接返回空;然后分为一空二不空、一不空二空、一二都不空三种情况构造新节点,最后递归地构造新二叉树
注意:递归构造前,先判断是否有空节点,若有则不再访问该空节点的孩子,直接将该空节点作为递归参数即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
func mergeTrees(root1 *TreeNode, root2 *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
if root1 == nil && root2 == nil {
return nil // 双方都是空
}
root := new(TreeNode) // 初始化根节点
if root1 == nil && root2 != nil { // 1空2不空
root.Val = root2.Val // 根节点赋值
} else if root1 != nil && root2 == nil { // 1不空2空
root.Val = root1.Val // 根节点赋值
} else { // 一二都不空
root.Val = root1.Val + root2.Val // 根节点赋值
}
if root1 == nil {
root.Left = mergeTrees(root1, root2.Left) // 构造根节点的左子树
root.Right = mergeTrees(root1, root2.Right) // 构造根节点的右子树
} else if root2 == nil {
root.Left = mergeTrees(root1.Left, root2) // 构造根节点的左子树
root.Right = mergeTrees(root1.Right, root2) // 构造根节点的右子树
} else {
root.Left = mergeTrees(root1.Left, root2.Left) // 构造根节点的左子树
root.Right = mergeTrees(root1.Right, root2.Right) // 构造根节点的右子树
}
return root
}
|
思路二:改造给定二叉树
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是两个二叉树的当前节点,返回值是新的节点
- 终止条件:两个二叉树的当前节点有一个为空
- 单层递归:判断两个二叉树的当前节点是否有空,若一方为空则直接返回另一方;节点值和赋值给树1,递归地构造新二叉树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
func mergeTrees(root1 *TreeNode, root2 *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
if root1 == nil {
return root2 // 直接返回树2的节点
}
if root2 == nil {
return root1 // 直接返回树1的节点
}
root1.Val += root2.Val // 更新树1节点值(中)
root1.Left = mergeTrees(root1.Left, root2.Left) // 更新树1的左孩子(左)
root1.Right = mergeTrees(root1.Right, root2.Right) // 更新树1的右孩子(右)
return root1
}
|
二叉搜索树中的搜索
700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点和一个目标值 ,在树中找到节点值等于目标值的节点后返回以该节点为根的子树, 若该节点不存在,则返回空节点
由于二叉搜索树左<父<右,所以前序先比较中,大的话向右搜索,小的话向左搜索,找到就返回
思路一
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是当前节点和目标值,不需要返回值,目标节点作为全局变量
- 终止条件:当前节点为空或找到目标节点
- 单层递归:判断当前节点为空的话,直接返回空节点;判断找到目标节点的话,直接返回目标节点;比较目标值与当前节点值,等于的话直接返回,大的话,向右递归搜索,小的话,向左递归搜索
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
var target *TreeNode
func searchBST(root *TreeNode, val int) *TreeNode {
target = new(TreeNode)
dfs(root, val)
if target.Val == 0 {
return nil // 节点不存在
}
return target
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode, val int) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
if target.Val != 0 {
return // 找到目标节点
}
if cur.Val == val {
target = cur // 找到目标节点
return
} else if cur.Val > val { // 当前节点值 > 目标值
dfs(cur.Left, val) // 向左搜索
} else { // 当前节点值 < 目标值
dfs(cur.Right, val) // 向右搜索
}
}
|
思路二
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是当前节点和目标值,返回值是目标节点
- 终止条件:当前节点为空或是目标节点
- 单层递归:判断当前节点为空或是目标节点的话,直接返回当前节点;比较目标值与当前节点值,大的话,向右递归搜索,小的话,向左递归搜索;当找到目标值或遇到空节点后,由于已经是递归函数逻辑上的最后一句,所以只会向上传递结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
func searchBST(root *TreeNode, val int) *TreeNode {
if root == nil || root.Val == val {
return root // 遇到空节点都没找到或找到目标节点
}
if root.Val > val {
return searchBST(root.Left, val) // 向左搜索
}
if root.Val < val {
return searchBST(root.Right, val) // 向右搜索
}
return nil // 程序不会执行到这
}
|
验证二叉搜索树
98. 验证二叉搜索树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树的根节点,判断其是否是一个二叉搜索树
由于是二叉搜索树,所以中序遍历结果是一个递增有序序列;由于二叉搜索树中根节点的左子树中所有节点都小于根节点、右子树中所有节点都大于根节点,所以不能单纯的只比较左节点小于中间节点,右节点大于中间节点,要用一个全局变量保存上一节点,保证中序遍历结果是一个有序序列
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是当前节点;返回值是布尔值,确定是否为二叉搜索树;记录上一节点值为全局变量
- 终止条件:遇到空节点
- 单层逻辑:若遇到空节点,直接返回真;向左递归遍历,若当前节点值大于中序序列中上一节点值说明符合规则,则更新记录上一节点值,否则直接返回假,该结果或由上层的变量接住,由每层最后return的向上传递;向右递归遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
var pre *TreeNode
func isValidBST(root *TreeNode) bool {
pre = nil
return dfs(root)
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode) bool {
// 判断是否遇到空节点
if cur == nil {
return true
}
// 向左递归
leftIsBST := dfs(cur.Left)
// 判断上一节点是否非空且大于等于当前节点值(中)
if pre != nil && pre.Val >= cur.Val {
return false
}
// 记录上一节点
pre = cur
// 向右递归
rightIsBST := dfs(cur.Right)
return leftIsBST && rightIsBST
}
|
二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给你一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,返回树中任意两不同节点值之间的最小差值
最小差值一定在相连接的节点间出现
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是当前节点;不需要返回值;上一节点和最小差值是全局变量
- 终止条件:遇到空节点
- 单层逻辑:判断是否遇到空节点,遇到的话直接返回;向左递归,用当前节点减去上一节点求得差值,与最小差值比较看是否需要更新;向右递归
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
var pre *TreeNode
var min int
func getMinimumDifference(root *TreeNode) int {
pre, min = nil, 100000
dfs(root)
return min
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
dfs(cur.Left) // 左
if pre != nil && cur.Val-pre.Val < min { // 中
min = cur.Val - pre.Val // 更新最小差值
}
pre = cur // 记录上一节点
dfs(cur.Right) // 右
}
|
二叉搜索树中的众数
501. 二叉搜索树中的众数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个含重复值的二叉搜索树的根节点,找出并返回 BST 中的所有众数(可能不止一个),此题的二叉搜索树左≤中≤右
思路一:当作普通树用map
遍历二叉搜索树,值存入map,遍历map找出结果
注意:要将等于最大频率的情况放到大于最大频率情况的前面,因为大于时会更新最大频率,若等于在其后会二次加入结果集
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
var mp map[int]int
func findMode(root *TreeNode) []int {
mp = make(map[int]int)
dfs(root)
max := 0 // 最大频率
res := make([]int, 0)
for k, v := range mp {
if v == max { // 等于最大频率
res = append(res, k) // 找到与当前最大频率相同的数
}
if v > max { // 大于最大频率
max = v // 更新最大频率
res = make([]int, 0) // 置空结果集
res = append(res, k) // 找到当前最大频率的数
}
}
return res
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
mp[cur.Val]++ // 中
dfs(cur.Left) // 左
dfs(cur.Right) // 右
}
|
思路二:利用二叉搜索树特性
二叉搜索树的中序序列是有序的,要遍历有序数组中元素出现的频率,只需比较相邻两个元素并统计频率,在树中也就是和前一个节点值作比较并统计频率,若等于最大频率则记录,大于最大频率则清空结果集并记录
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
var maxCount int
var count int
var pre *TreeNode
var res []int
func findMode(root *TreeNode) []int {
maxCount, count, pre = 0, 0, nil
res = make([]int, 0)
dfs(root)
return res
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
dfs(cur.Left) // 左
if pre == nil { // 是第一个节点
count = 1 // 计数
} else if pre.Val == cur.Val { // 与上一节点值相等
count++ // 更新计数
} else { // 是一个新数
count = 1 // 重新计数
}
pre = cur // 记录上一节点
if count == maxCount { // 当前节点值频率等于最大频率
res = append(res, cur.Val) // 记录当前节点值
}
if count > maxCount { // 当前节点值频率大于最大频率
maxCount = count // 更新最大频率
res = make([]int, 0) // 置空结果集
res = append(res, cur.Val) // 记录当前节点值
}
dfs(cur.Right) // 右
}
|
二叉树的最近公共祖先
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树,找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先,公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)
后序遍历,终止条件会用到当前节点,相当于后序结合前序,左右子树找到的结果汇总在中进行处理
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是当前节点和两个指定节点;返回值是找到的指定节点或其最近公共祖先
- 终止条件:遇到空节点或指定节点
- 单层逻辑:判断是否遇到空节点,若遇到直接返回空;判断是否遇到指定节点,若遇到直接返回该节点;向左递归找指定节点;向右递归找指定节点;若左右子树都找到指定节点说明该节点是最近公共祖先,返回该节点;若左右子树有一个找到指定节点,则返回找到的该节点;若左右子树都没找到,则返回空
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
func lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
if root == p || root == q { // 中
return root
}
left := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Left, p, q) // 左
right := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Right, p, q) // 右
if left != nil && right != nil { // 左右都不空(中)
return root
}
if left == nil && right != nil { // 左空右不空
return right
}
if left != nil && right == nil { // 左不空右空
return left
}
return nil // 左右都空
}
|
二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉搜索树,找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先
二叉搜索树可以确定搜索方向,因为是有序树,所以只要从上到下去遍历(前序),遇到节点值在[p, q]区间中,则一定可以说明该节点就是p和q的最近公共祖先,因为若继续向左或向右都会错过成为另一目标节点的祖先
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是当前节点和目标值;返回值是找到的最近公共祖先
- 终止条件:遇到空节点;由于一定会找到,也可以不需要终止条件
- 单层逻辑:判断当前节点是否大于p和q,若是则向左递归搜索,若返回值非空说明找到最近公共祖先,直接返回;判断当前节点是否小于p和q,若是则向右递归搜索,若返回值非空说明找到最近公共祖先,直接返回;程序执行到此处说明当前节点在
[p,q]中,当前节点就是最近公共祖先,直接返回该节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
func lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
if root.Val > p.Val && root.Val > q.Val {
left := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Left, p, q) // 左
if left != nil {
return left
}
}
if root.Val < p.Val && root.Val < q.Val {
right := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Right, p, q) // 右
if right != nil {
return right
}
}
return root // 找到最近公共祖先
}
|
二叉搜索树中的插入操作
701. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定二叉搜索树的根节点和要插入的值,返回插入后的根节点,要插入的值和二叉搜索树中的任意节点值都不同
遍历二叉搜索树,找到空节点插入元素就可以了,可以不考虑修改树的结构
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是当前节点和要插入的值;返回插入的节点
- 终止条件:遇到空节点
- 单层逻辑:判断是否遇到空节点,若遇到则插入节点后返回;若当前节点值大于插入值,则向左递归,用当前节点的左孩子接住;若当前节点值小于插入值,则向右递归,用当前节点的右孩子接住;最后返回当前节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
func insertIntoBST(root *TreeNode, val int) *TreeNode {
// 判断是否遇到空节点
if root == nil {
// 返回新节点
return &TreeNode{Val: val}
}
// 向左/右递归
if root.Val < val {
root.Right = insertIntoBST(root.Right, val)
} else {
root.Left = insertIntoBST(root.Left, val)
}
return root
}
|
删除二叉搜索树中的节点
450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定二叉搜索树的根节点和一个目标值,删除树中目标值对应的节点,返回根节点,树的结构可能需要被调整以满足二叉搜索树特性
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是当前节点和目标值;返回值是删除节点后此位置的节点;通过递归函数的返回值来移除节点
- 终止条件:遇到空节点
- 单层逻辑:判断是否遇到空节点,若遇到说明没找到要删除的节点,直接返回空;若当前节点值等于目标值,分四种情况处理;若当前节点大于目标值;向左递归,用当前节点的左孩子接住删除节点后此位置的节点;若当前节点小于目标值;向右递归,用当前节点的右孩子接住删除节点后此位置的节点;最后返回当前节点
- 第一种情况:要删除节点的左右孩子都为空(叶子节点),返回空,表示直接删除
- 第二种情况:要删除节点的左孩子为空,右孩子不为空,删除节点,右孩子补位,返回右孩子为根节点
- 第三种情况:要删除节点的右孩子为空,左孩子不为空,删除节点,左孩子补位,返回左孩子为根节点
- 第四种情况:要删除节点的左右孩子节点都不为空,则将要删除节点的左子树头结点(左孩子)放到删除节点的右子树的最左面节点的左孩子上,返回要删除节点的右孩子为新的根节点;因为要删除节点的右子树所有节点都比要删除的节点大,而其最左面的节点是最小的节点,仅大于要删除的节点,而要删除节点的左子树所有节点都比要删除的节点小,所以放到要删除节点的左孩子上
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
func deleteNode(root *TreeNode, key int) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
if root.Val == key {
// 判要删除节点的右孩子是否为空
if root.Right == nil {
// 直接返回左孩子
return root.Left
} else {
cur := root.Right
for cur != nil && cur.Left != nil {
cur = cur.Left
} // cur此时指向要删除节点的右子树的最左子节点
// 要删除节点的左子树放到右子树的最左子节点
cur.Left = root.Left
return root.Right
}
}
if root.Val > key {
root.Left = deleteNode(root.Left, key)
} else {
root.Right = deleteNode(root.Right, key)
}
return root
}
|
修剪二叉搜索树
669. 修剪二叉搜索树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定二叉搜索树的根节点,同时给定最小边界和最大边界,通过修剪二叉搜给定区间中,返回根节点
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是当前节点和边界;返回值是完成修剪后此位置的节点;通过递归函数的返回值来移除节点
- 终止条件:遇到空节点
- 单层逻辑:判断是否为空,若为空直接返回空;判断当前节点值是否小于左边界,若是则说明要删除该节点,向该节点的右子树中寻找满足区间条件的节点返回,上一层节点的对应孩子会接住该返回值(删除操作);判断当前节点值是否大于右边界,若是则说明要删除该节点,向该节点的左子树中寻找满足区间条件的节点返回,上一层节点的对应孩子会接住该返回值(删除操作);正常向左递归,用当前节点左孩子接住符合条件的左孩子;正常向右递归,用当前节点右孩子接住符合条件的右孩子;最后返回当前节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
func trimBST(root *TreeNode, low int, high int) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return nil // 遇到空节点
}
if root.Val < low { // 当前节点值小于左边界
return trimBST(root.Right, low, high) // 向右子树寻找符合条件的节点
}
if root.Val > high { // 当前节点值大于右边界
return trimBST(root.Left, low, high) // 向左子树寻找符合条件的节点
}
root.Left = trimBST(root.Left, low, high) // 向左递归
root.Right = trimBST(root.Right, low, high) // 向右递归
return root
}
|
将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个升序整数数组,将其转换为一棵平衡二叉搜索树,平衡二叉树是指该树所有节点的左右子树的深度相差不超过 1
要构成构成平衡二叉搜索树,可以从升序数组中间位置取值作为根,本质就是寻找分割点,分割点作为当前节点,然后递归左区间和右区间
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是给定数组和本树的区间;返回值是构造的节点
- 终止条件:左边界大于右边界
- 单层逻辑:判断区间左边界是否大于右边界,若大于说明该分支构造完成则直接返回空;根据目前的左右边界求得中间索引,用目前区间中间值构造新节点;向左递归,用当前中间值的左边所有元素构造左子树,用当前新构造节点的左孩子接住返回值;向右递归,用当前中间值的右边所有元素构造右子树,用当前新构造节点的右孩子接住返回值;最后返回当前节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
func sortedArrayToBST(nums []int) *TreeNode {
root := dfs(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
return root
}
func dfs(nums []int, left int, right int) *TreeNode {
if left > right {
return nil // 构造完成
}
mid := left + ((right - left) / 2) // 当前区间中间索引
node := new(TreeNode)
node.Val = nums[mid] // 新构造节点赋值
node.Left = dfs(nums, left, mid-1) // 向左递归构造左子树
node.Right = dfs(nums, mid+1, right) // 向右递归构造右子树
return node // 返回当前节点
}
|
把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
538. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给出二叉搜索树的根节点,该树的节点值各不相同,将其转换为累加树,每个节点的新值是原树中大于或等于旧值的数之和
由于是二叉搜索树,所以比当前节点大的值都在其右边,求新值也就是将旧值加上其右边所有值之和;若按照右中左的顺序遍历,每次只需用当前元素值加上其上一元素值即可得到新值
- 递归参数和返回值:参数是当前节点;不需要返回值;全局变量保存上一节点值
- 终止条件:遇到空节点
- 单层逻辑:判断是否为空,若是直接返回;向右递归遍历;若上一节点不为空,则将更新当前节点值=当前节点值+上一节点值;更新上一节点值;向左递归遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
var pre int
func convertBST(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
pre = 0
dfs(root)
return root
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode) {
if cur == nil {
return // 遇到空节点
}
dfs(cur.Right) // 右
cur.Val += pre // 更新当前节点值(中)
pre = cur.Val // 记录上一节点值
dfs(cur.Left) // 左
}
|
附加
二叉树中的最大路径和
124. 二叉树中的最大路径和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树,返回树中的最大路径和,路径起点和终点随意,节点值有正有负
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
// 写法一
var maxVal int
func maxPathSum(root *TreeNode) int {
// 初始化最大路径和为最小负数
maxVal = math.MinInt
dfs(root)
return maxVal
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode) int {
if cur == nil {
// 遇到空节点
return 0
}
// 返回当前节点左子树中的最大路径和(左)
leftVal := dfs(cur.Left)
// 返回当前节点右子树中的最大路径和(右)
rightVal := dfs(cur.Right)
// 更新当前节点作为树根节点的最大路径和(中)
maxVal = max(maxVal, leftVal+rightVal+cur.Val)
// 返回当前节点作为一条链端点的最大路径和
// 因为有可能为负数,所以和0比较
// 若为负数,则取0,表示不选该节点/该节点作为根节点的树
return max(max(leftVal, rightVal)+cur.Val, 0)
}
// 写法二(推荐,易懂)
func maxPathSum(root *TreeNode) int {
res := -1001
var dfs func(*TreeNode) int
dfs = func(cur *TreeNode) int {
if cur == nil {
return 0
}
left := dfs(cur.Left)
right := dfs(cur.Right)
res = max(res, cur.Val+left+right, cur.Val+left, cur.Val+right, cur.Val)
cur.Val = max(cur.Val, cur.Val+left, cur.Val+right)
return cur.Val
}
dfs(root)
return res
}
|
- 时间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中 $n$ 为二叉树的节点个数
- 空间复杂度:$O(n)$,最坏情况下,二叉树退化成一条链,递归需要 $O(n)$ 的栈空间
附加
不同的二叉搜索树 II
95. 不同的二叉搜索树 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个整数 n ,生成并返回所有由 n 个节点组成且节点值从 1 到 n 互不相同的不同 二叉搜索树
进入递归,遍历1-n,将每个数字作为根节点,更新区间,向左向右递归得到左右子树,最后左右子树两两组合;若区间内无节点,则将空入集返回;若区间只有一个节点,则将该节点入集返回;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
func generateTrees(n int) []*TreeNode {
return getAns(1, n)
}
// getAns 函数递归生成从 start 到 end 范围内所有可能的二叉搜索树
func getAns(start, end int) []*TreeNode {
var ans []*TreeNode
// 此时没有数字,将 nil 加入结果中
if start > end {
ans = append(ans, nil)
return ans
}
// 只有一个数字,当前数字作为一棵树加入结果中
if start == end {
tree := &TreeNode{Val: start}
ans = append(ans, tree)
return ans
}
// 尝试每个数字作为根节点
for i := start; i <= end; i++ {
// 得到所有可能的左子树
leftTrees := getAns(start, i-1)
// 得到所有可能的右子树
rightTrees := getAns(i+1, end)
// 左子树右子树两两组合
for _, leftTree := range leftTrees {
for _, rightTree := range rightTrees {
root := &TreeNode{Val: i}
root.Left = leftTree
root.Right = rightTree
// 加入到最终结果中
ans = append(ans, root)
}
}
}
return ans
}
|
求根节点到叶节点数字之和
129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,树中每个节点都存放有一个 0 到 9 之间的数字。每条从根节点到叶节点的路径都代表一个数字:例如,从根节点到叶节点的路径 1 -> 2 -> 3 表示数字 123 。计算从根节点到叶节点生成的 所有数字之和
思路:DFS前序遍历中带回溯,当遇到叶子节点时收集结果,收集后回溯路径中的当前叶子节点值;在向左右递归前,判断是否为空;向左右递归结束后,回溯当前非叶子节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
var path []int
var res int
func sumNumbers(root *TreeNode) int {
path, res = make([]int, 0), 0
dfs(root)
return res
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode) {
// 中
path = append(path, cur.Val)
// 判断是否遇到叶子节点
if cur.Left == nil && cur.Right == nil {
// 收集结果
sum := 0
for _, v := range path {
sum = sum*10 + v
}
res += sum
// 回溯当前叶子节点
path = path[:len(path)-1]
// 返回上一层
return
}
// 判断是否有左孩子
if cur.Left != nil {
// 向左递归
dfs(cur.Left)
}
// 判断是否有右孩子
if cur.Right != nil {
// 向右递归
dfs(cur.Right)
}
// 回溯当前非叶子节点
path = path[:len(path)-1]
}
|
将二叉搜索树变平衡
1382. 将二叉搜索树变平衡 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一棵二叉搜索树,返回一棵 平衡后 的二叉搜索树。如果有多种构造方法,请你返回任意一种。如果一棵二叉搜索树中,每个节点的两棵子树高度差不超过 1 ,就称这棵二叉搜索树是 平衡的
思路:中序遍历把二叉树转变为有序数组,然后在根据有序数组构造平衡二叉搜索树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
var nums []int
func balanceBST(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
nums = make([]int, 0)
// 有序树转成有序数组(中序)
dfs(root)
// 有序数组转平衡二叉树
return createAVL(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
}
func dfs(cur *TreeNode) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
dfs(cur.Left)
nums = append(nums, cur.Val)
dfs(cur.Right)
}
func createAVL(nums []int, left, right int) *TreeNode {
if left > right {
return nil
}
// 当前区间中间索引
mid := left + (right-left)/2
node := new(TreeNode)
// 新构造节点赋值
node.Val = nums[mid]
// 向左递归构造左子树
node.Left = createAVL(nums, left, mid-1)
// 向右递归构造右子树
node.Right = createAVL(nums, mid+1, right)
// 返回当前节点
return node
}
|
二叉树的直径
543. 二叉树的直径 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一棵二叉树的根节点,返回该树的 直径 。二叉树的 直径 是指树中任意两个节点之间最长路径的 长度 。这条路径可能经过也可能不经过根节点 root 。两节点之间路径的 长度 由它们之间边数表示
思路:DFS后序遍历,在中间节点将其左右子树两链(高度)连接,合并后长度与目前记录的最长长度比较取最大值,最后返回左右子树高度中的大值
注意:叶子节点高度为0;DFS后+1作为当前节点的高度
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
func diameterOfBinaryTree(root *TreeNode) int {
res := 0
var dfs func(cur *TreeNode) int
dfs = func(cur *TreeNode) int {
if cur == nil {
// 下面+1,对于叶子节点高度为0
return -1
}
// 左右子树高度
lLen := dfs(cur.Left) + 1
rLen := dfs(cur.Right) + 1
// 合成两链比较更新最长路径
res = max(res, lLen+rLen)
// 返回左右子树最大高度
return max(lLen, rLen)
}
dfs(root)
return res
}
|
二叉搜索树中第 K 小的元素
230. 二叉搜索树中第 K 小的元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,和一个整数 k ,查找其中第 k 小的元素(从 1 开始计数)
思路:中序,在中数k,数到k后收集目标节点值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
func kthSmallest(root *TreeNode, k int) int {
res := -1
var dfs func(cur *TreeNode)
dfs = func(cur *TreeNode) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
dfs(cur.Left)
if k == 0 {
return
}
k--
if k == 0 {
res = cur.Val
}
dfs(cur.Right)
}
dfs(root)
return res
}
|
二叉树展开为链表
114. 二叉树展开为链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定二叉树的根结点 root ,将它展开为一个单链表:
- 展开后的单链表应该同样使用 TreeNode ,其中 right 子指针指向链表中下一个结点,而左子指针始终为 null 。
- 展开后的单链表应该与二叉树 先序遍历 顺序相同
思路:找左子树的最右节点
- 前序遍历访问各节点的顺序是根节点、左子树、右子树。如果一个节点的左子节点为空,则该节点不需要进行展开操作。
- 如果一个节点的左子节点不为空,则该节点的左子树中的最后一个节点被访问之后,该节点的右子节点被访问。
- 该节点的左子树中最后一个被访问的节点是左子树中的最右边的节点,也是该节点的右子节点的前驱节点。因此,问题转化成寻找当前节点的右子节点的前驱节点。
- 具体做法是,对于当前节点,如果其左子节点不为空,则在其左子树中找到最右边的节点,作为前驱节点,将当前节点的右子节点赋给前驱节点的右子节点,然后将当前节点的左子节点赋给当前节点的右子节点,并将当前节点的左子节点设为空。
- 对当前节点处理结束后,继续处理链表中的下一个节点,直到所有节点都处理结束
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
// 写法一
func flatten(root *TreeNode) {
cur := root
for cur != nil {
// 判当前节点左子树是否为空
if cur.Left != nil {
// 初始化当前节点左子树的最右子节点为当前节点的左子节点
right := cur.Left
// 不断向右搜索
for right.Right != nil {
right = right.Right
}
// 将当前节点的右子树作为当前节点左子树的最右节点的右子树
right.Right = cur.Right
// 将更新后的当前节点的左子树作为右子树
cur.Right = cur.Left
// 清空左子树
cur.Left = nil
}
// 当前节点继续向右搜索
cur = cur.Right
}
}
// 写法二:DFS中序 (推荐)
func flatten(root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return
}
flatten(root.Left)
if root.Left != nil {
temp := root.Right
root.Right = root.Left
root.Left = nil
// 找最右下的节点
cur := root
for cur.Right != nil {
cur = cur.Right
}
cur.Right = temp
}
flatten(root.Right)
}
|
路径总和 III
437. 路径总和 III - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,和一个整数 targetSum ,求该二叉树里节点值之和等于 targetSum 的 路径 的数目。路径 不需要从根节点开始,也不需要在叶子节点结束,但是路径方向必须是向下的(只能从父节点到子节点)
思路:本题做法和 560 题是一样的,前缀和+哈希表。
在二叉树上,前缀和相当于从根节点开始的路径元素和。用哈希表 cnt 统计前缀和的出现次数,当我们递归到节点 node 时,设从根到 node 的路径元素和为 s,那么就找到了 cnt[s−targetSum] 个符合要求的路径,加入答案
注意:
- 要初始化哈希表[0] = 1中。因为这里的 0 相当于前缀和数组中的 s[0]=0。举个最简单的例子,根节点值为 1,targetSum=1。如果不把 0 加到哈希表中,按照我们的算法,没法算出这里有 1 条符合要求的路径。也可以这样理解,要想把任意路径和都表示成两个前缀和的差,必须添加一个 0,否则当路径是前缀时(从根节点开始的路径),没法减去一个数,具体见 前缀和及其扩展 中的讲解。
- 代码中要先更新 ans,再更新 cnt。因为在 targetSum=0 的情况下,这俩谁先谁后都可以。但如果 targetSum=0,假设根节点值为 1,如果先把 cnt[1] 增加 1,再把 ans 增加 cnt[s−targetSum]=cnt[1]=1,就相当于找到了一条和为 targetSum=0 的路径,但和为 0 的路径是不存在的。
- 递归完左右子节点后要删除当前路径和在哈希中的次数。因为如果不恢复现场,当递归完左子树,要递归右子树时,cnt 中还保存着左子树的数据。但递归到右子树,要计算的路径并不涉及到左子树的任何节点,如果不恢复现场,cnt 中统计的前缀和个数会更多,算出来的答案可能比正确答案更大
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
func pathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) int {
res := 0
mp := map[int]int{0: 1}
var dfs func(*TreeNode, int)
dfs = func(cur *TreeNode, sum int) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
sum += cur.Val
res += mp[sum-targetSum]
mp[sum]++
dfs(cur.Left, sum)
dfs(cur.Right, sum)
mp[sum]--
}
dfs(root, 0)
return res
}
|
二叉树的序列化与反序列化
297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化 - 力扣(LeetCode)
JZ37 序列化二叉树_牛客题霸_牛客网
给定一个二叉树,将其序列化输出,再按照该序列化输出反序列化出二叉树
BFS
序列化:用队列层次遍历二叉树
- 若遇到非空节点,则节点值加入结果集,左右孩子入队
- 若遇到空节点,则标记
x加入结果集
反序列化:用指针curIdx标记当前队首节点的左孩子在序列中的位置,指针每次前进二个单位
注意:由于负数没有对应的字符,所有只能用字符串作为结果集元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
|
type Codec struct {
}
func Constructor() Codec {
var codec Codec
return codec
}
// Serializes a tree to a single string.
func (this *Codec) serialize(root *TreeNode) string {
// 由于负数无法与字符对应所有只能用字符串
res := make([]string, 0)
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
queue = append(queue, root)
for len(queue) != 0 {
// 取队首
cur := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
// 判是否为非空节点
if cur != nil {
// 非空节点值加入结果集 左右孩子直接入队
res = append(res, strconv.Itoa(cur.Val))
queue = append(queue, cur.Left)
queue = append(queue, cur.Right)
} else {
// 空节点标记为x加入结果集
res = append(res, "x")
}
}
fmt.Println(res)
return strings.Join(res, ",")
}
// Deserializes your encoded data to tree.
func (this *Codec) deserialize(data string) *TreeNode {
if data == "x" {
return nil
}
// 字符串转为字符串切片(去掉分隔符)
list := strings.Split(data, ",")
// 初始化根节点
val, _ := strconv.Atoi(list[0])
root := &TreeNode{Val: val}
// 创建队列根节点入队
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
queue = append(queue, root)
// 标记当前根节点的左子节点位置
curIdx := 1
// 从第二个节点开始遍历
for curIdx < len(list) {
// 取队首
node := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
// 判左子节点非空
if list[curIdx] != "x" {
// 初始化当前节点的左子节点
v, _ := strconv.Atoi(list[curIdx])
newNode := &TreeNode{Val: v}
node.Left = newNode
// 左子节点入队
queue = append(queue, newNode)
}
// 判右子节点非空
if list[curIdx+1] != "x" {
// 初始化当前节点的右子节点
v, _ := strconv.Atoi(list[curIdx+1])
newNode := &TreeNode{Val: v}
node.Right = newNode
// 右子节点入队
queue = append(queue, newNode)
}
// 标记队中下一节点的左子节点位置
curIdx += 2
}
return root
}
|
DFS
序列化:前序遍历二叉树
- 若遇到非空节点,则节点值加入结果集,向深搜索左右孩子
- 若遇到空节点,则标记
x加入结果集
下面代码采用在根节点合并左右子树的方式,没有采用上面的逐个添加到结果集的方式
反序列化:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
type Codec struct {
}
func Constructor() Codec {
var codec Codec
return codec
}
// Serializes a tree to a single string.
func (this *Codec) serialize(root *TreeNode) string {
// 判当前节点是否为空
if root == nil {
return "x"
}
// 前序遍历 在根节点拼接
return strconv.Itoa(root.Val) + "," + this.serialize(root.Left) + "," + this.serialize(root.Right)
}
// Deserializes your encoded data to tree.
func (this *Codec) deserialize(data string) *TreeNode {
// 将字符串转成字符串切片(去分隔符)
list := strings.Split(data, ",")
// 前序递归构建树
// 注意传入切片地址(值拷贝只能传递切片结构副本)
return buildTree(&list)
}
func buildTree(list *[]string) *TreeNode {
// 取头节点
cur := (*list)[0]
*list = (*list)[1:]
// 判是否为空
if cur == "x" {
return nil
}
v, _ := strconv.Atoi(cur)
// 创建新节点
root := &TreeNode{Val: v}
// 递归构建左右子节点
root.Left = buildTree(list)
root.Right = buildTree(list)
return root
}
|
二叉搜索树迭代器
173. 二叉搜索树迭代器 - 力扣(LeetCode)
实现一个二叉搜索树迭代器类BSTIterator ,表示一个按中序遍历二叉搜索树(BST)的迭代器:
BSTIterator(TreeNode root) 初始化 BSTIterator 类的一个对象。BST 的根节点 root 会作为构造函数的一部分给出。指针应初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,且该数字小于 BST 中的任何元素。boolean hasNext() 如果向指针右侧遍历存在数字,则返回 true ;否则返回 false 。int next()将指针向右移动,然后返回指针处的数字。
注意,指针初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,所以对 next() 的首次调用将返回 BST 中的最小元素。
你可以假设 next() 调用总是有效的,也就是说,当调用 next() 时,BST 的中序遍历中至少存在一个下一个数字
思路一:DFS 中序 + 存储序列 (不推荐)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
type BSTIterator struct {
nums []int
idx int
}
func Constructor(root *TreeNode) BSTIterator {
bSTIterator := BSTIterator{
nums: []int{},
idx: 0,
}
var dfs func(*TreeNode)
dfs = func(cur *TreeNode) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
dfs(cur.Left)
bSTIterator.nums = append(bSTIterator.nums, cur.Val)
dfs(cur.Right)
}
dfs(root)
return bSTIterator
}
func (this *BSTIterator) Next() int {
val := this.nums[this.idx]
this.idx++
return val
}
func (this *BSTIterator) HasNext() bool {
return this.idx < len(this.nums)
}
|
- 时间复杂度:构造函数是 O(N);调用
next() 方法的时间复杂度是 O(1)。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),保存了所有元素
思路二:斜DFS + 栈(推荐)
步骤:
- 斜DFS:从当前节点->最左下节点遍历一次,将本次遍历结果存入栈;
- next:弹栈,若弹栈的节点有右孩子,则对右孩子来一次斜DFS,结果同样存入栈
- hasNext:判栈是否非空即可
分析:
- 节省时间:边遍历得到中序序列,边next判断,不必事先全部DFS中序遍历一遍
- 节省空间:栈中最多只保存树高度的节点,不用保存树中所有节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
type BSTIterator struct {
stack []*TreeNode
}
func Constructor(root *TreeNode) BSTIterator {
bSTIterator := BSTIterator{
stack: []*TreeNode{},
}
for root != nil {
bSTIterator.stack = append(bSTIterator.stack, root)
root = root.Left
}
return bSTIterator
}
func (this *BSTIterator) Next() int {
node := this.stack[len(this.stack)-1]
this.stack = this.stack[:len(this.stack)-1]
if node.Right != nil {
cur := node.Right
for cur != nil {
this.stack = append(this.stack, cur)
cur = cur.Left
}
}
return node.Val
}
func (this *BSTIterator) HasNext() bool {
return len(this.stack) > 0
}
|
- 时间复杂度:均摊复杂度是 O(1),调用 next() 方法的时候,如果栈顶元素有右子树,则把所有右边节点即其所有左孩子全部放到了栈中,下次调用 next() 的时候,直接访问栈顶就可以了,均摊之后时间复杂度是 O(1)。
- 空间复杂度:O(h),h 为树的高度,因为栈中只保留了左节点,栈中元素最多的时候,就是树的高度
叶子相似的树
872. 叶子相似的树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定两个树,比较其叶子是否相等
思路:dfs保存叶子序列后逐个比较
注意:由于是左右均为空返回,所以记得在前先判断当前节点是否为空,防止一侧有孩子一侧没孩子,左右不全空,进入空的左右会空指针异常
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
func leafSimilar(root1 *TreeNode, root2 *TreeNode) bool {
nums1, nums2 := []int{}, []int{}
var dfs1 func(cur *TreeNode)
dfs1 = func(cur *TreeNode) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
if cur.Left == nil && cur.Right == nil {
nums1 = append(nums1, cur.Val)
return
}
dfs1(cur.Left)
dfs1(cur.Right)
}
var dfs2 func(cur *TreeNode)
dfs2 = func(cur *TreeNode) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
if cur.Left == nil && cur.Right == nil {
nums2 = append(nums2, cur.Val)
return
}
dfs2(cur.Left)
dfs2(cur.Right)
}
dfs1(root1)
dfs2(root2)
if len(nums1) != len(nums2) {
return false
}
for i, v := range nums1 {
if v != nums2[i] {
return false
}
}
return true
}
|
统计二叉树中好节点的数目
1448. 统计二叉树中好节点的数目 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一棵根为 root 的二叉树,返回二叉树中好节点的数目。「好节点」X 定义为:从根到该节点 X 所经过的节点中,没有任何节点的值大于 X 的值
思路:dfs+递归参数中记录根到当前节点路径中的最大值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
func goodNodes(root *TreeNode) int {
res := 0
var dfs func(*TreeNode, int)
dfs = func(cur *TreeNode, pathMax int) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
if cur.Val >= pathMax {
res++
pathMax = cur.Val
}
dfs(cur.Left, pathMax)
dfs(cur.Right, pathMax)
}
dfs(root, math.MinInt)
return res
}
|
二叉树中的最长交错路径
1372. 二叉树中的最长交错路径 - 力扣(LeetCode)
左右交错遍历二叉树,返回最长交错路径,交错路径定义为访问过的节点数目-1
思路:dfs
每次往子节点递归时,只有往与之前的方向相反长度才能在之前的基础上增加,否则就相当于以当前节点为一个新的起点去搜索
注意:从根节点开始,到达根节点时的长度为0,是否为左子节点不影响结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
func longestZigZag(root *TreeNode) int {
res := 0
var dfs func(*TreeNode, int, bool)
dfs = func(cur *TreeNode, depth int, isLeft bool) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
res = max(res, depth)
if isLeft {
dfs(cur.Right, depth+1, false)
dfs(cur.Left, 1, true)
} else {
dfs(cur.Left, depth+1, true)
dfs(cur.Right, 1, false)
}
}
dfs(root, 0, true)
return res
}
|
最大层内元素和
1161. 最大层内元素和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
返回层内元素之和最大的一层的层号,层元素和相同时取层号最小的
思路:BFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
func maxLevelSum(root *TreeNode) int {
res := 1
maxSum := math.MinInt
depth := 1
queue := []*TreeNode{root}
for len(queue) != 0 {
cnt := len(queue)
sum := 0
for i := 0; i < cnt; i++ {
sum += queue[0].Val
if queue[0].Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Left)
}
if queue[0].Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[0].Right)
}
queue = queue[1:]
}
if sum > maxSum {
res = depth
maxSum = sum
}
depth++
}
return res
}
|
字典序排数
386. 字典序排数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给一个整数 n ,按字典序返回范围 [1, n] 内所有整数。必须设计一个时间复杂度为 O(n) 且使用 O(1) 额外空间的算法
思路:DFS
宫水三叶的题解
将 [1,n] 的数按照字典序添加到答案,本质上是对一颗节点数量为 n,形态类似字典树的多阶树进行遍历,根节点为 0,需要被跳过,因此可以从树的第二层开始搜索
树中每个节点的值为其搜索路径所代表的数字,且每个节点有 [0,9] 共 10 个子节点,值为上一层节点值×10+i
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
func lexicalOrder(n int) []int {
res := []int{}
var dfs func(int)
dfs = func(cur int) {
if cur > n {
return
}
// 将当前节点加入结果集
res = append(res, cur)
// 遍历当前层全部0~9作为根节点,共10个节点
for i := 0; i <= 9; i++ {
// 下一层节点值=当前节点值*10加下一层节点值
dfs(cur*10 + i)
}
}
// 遍历第二层1~9作为根节点,共9个节点
for i := 1; i <= 9; i++ {
dfs(i)
}
return res
}
|
二叉搜索树与双向链表⚪
JZ36 二叉搜索树与双向链表_牛客题霸_牛客网
输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表,树中节点的左指针即前驱,右指针即后继,返回链表中的第一个节点的指针。要求:空间复杂度O(1)(即在原树上操作),时间复杂度 O(n)
LCR 155. 将二叉搜索树转化为排序的双向链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
426. 将二叉搜索树转化为排序的双向链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
与上面区别是首尾也要相连
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
func Convert( pRootOfTree *TreeNode ) *TreeNode {
if pRootOfTree == nil {
return nil
}
dummyNode := new(TreeNode)
pre := dummyNode
var dfs func(*TreeNode)
dfs = func(cur *TreeNode) {
if cur == nil {
return
}
dfs(cur.Left)
cur.Left = pre
pre.Right = cur
pre = cur
dfs(cur.Right)
}
dfs(pRootOfTree)
res := dummyNode.Right
dummyNode.Right.Left = nil
return res
}
|
二叉树的下一个结点⚫
二叉树的下一个结点_牛客题霸_牛客网
给定一个二叉树其中的一个结点,请找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点并且返回。注意,树中的结点不仅包含左右子结点,同时包含指向父结点的next指针。
输入不给根节点,给的是目标节点,但每个节点有指向父结点的next指针
思路:
- 若给出的结点有右子节点,则最终要返回的下一个结点即右子树的最左下的结点
- 若给出的结点无右子节点,且当前结点是其父节点的左子节点,则返回其父节点
- 若给出的结点无右子节点,且当前结点是其父节点的右子节点,则先要沿着左上方父节点爬树,一直爬到当前结点是其父节点的左子节点为止,返回的就是这个父节点;或者没有满足上述情况的则返回为NULL
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
func GetNext(pNode *TreeLinkNode) *TreeLinkNode {
if pNode.Right != nil {
cur := pNode.Right
for cur.Left != nil {
cur = cur.Left
}
return cur
}
if pNode.Next != nil && pNode.Next.Left == pNode {
return pNode.Next
}
for pNode.Next != nil && pNode.Next.Left != pNode {
pNode = pNode.Next
}
return pNode.Next
}
|
二叉搜索树中的中序后继
LCR 053. 二叉搜索树中的中序后继
面试题 04.06. 后继者 - 力扣(LeetCode)
285. 二叉搜索树中的中序后继 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树的根节点和目标结点,找出中序遍历目标结点的下一个结点并且返回。
思路一:中序遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
func inorderSuccessor(root *TreeNode, p *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
var pre *TreeNode
var dfs func(*TreeNode) *TreeNode
dfs = func(cur *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
if cur == nil {
return nil
}
left := dfs(cur.Left)
if pre != nil && pre == p {
pre = cur
return cur
}
pre = cur
right := dfs(cur.Right)
if left == nil {
return right
}
return left
}
return dfs(root)
}
|
思路二:利用二叉搜索树性质
- 若目标节点存在右子树,则中序遍历的后继结点一定是右子树的最左节点
- 若目标节点不存在右子树,则从根节点开始向下遍历
- 若当前节点值大于目标节点,说明目标的后继结点可能为当前节点或在当前节点的左子树,更新结果为当前节点,然后向左递归
- 若当前节点值小于目标节点,说明目标的后继结点在当前节点的右子树,向右递归
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
func inorderSuccessor(root *TreeNode, p *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
if p.Right != nil {
cur := p.Right
for cur.Left != nil {
cur = cur.Left
}
return cur
}
var res *TreeNode
cur := root
for cur != nil {
if cur.Val > p.Val {
res = cur
cur = cur.Left
} else {
cur = cur.Right
}
}
return res
}
|




